1. We'll now venture off on an involved mathematical journey and identify some recorded history, which has massive implications to all 3 of the main pyramids of the Giza Plateau.
2. The father of profane history, the Greek historian Herodotus, visited Egypt and, after consultation with Egyptian Priests, recorded two mathematical attributes of the Great Pyramid. These were:
3. He recorded that the surface area of each face was 8 Egyptian acres.
4. He recorded that the surface area of each face was equal to the square of the height.
5. In the, almost, 2500 years since Herodotus wrote down these snippets of information, no-one has been able to make the statements fit extant attributes of the Great Pyramid effectively. The prevailing attitude from the scientific community has been that Herodotus should have stuck to his forté of recording history, rather than dabbling in mathematical concepts to which he was, obviously, unsuited.
6. As it turns out, Herodotus was perfectly correct and it is the modern theorists, trying to apply the wrong measurement standard to the pyramids, who are in error. Let's put Herodotus to the test:
7. To find the area of 1 side of the Great Pyramid the intended and encrypted formula was to consider the base length to be 756 feet, the side diagonal length to be 576 feet and the flat floor top to be 44 feet. Therefore, the simple formula for finding the side area is 756 + 44 = 800 ÷ 2 = 400... X 576 = 230400 square feet.
8. Herodotus tells us that this square footage equals 8 Egyptian acres, therefore, 230400 ÷ 8 = 28800 sq. ft.
9. It comes as no surprise that the number chosen by our ancient forebears upon which to build the Pyramid Acre is one of the most dynamic and universally used numbers of antiquity...288*.
Having ascertained that the area of 28800 square feet constitutes a "pyramid acre", how many pyr. acres are there for all 4 sides, as well as the base area occupied by the pyramid?
The number of pyr. acres for 4 sides = 32 + the pyr. acre area of the base (756 X 756 ÷ 28800 = 19.845) = 51.845 acres total. So the 51.84-degree side angle is coded yet again in the acreage value. It is also found as a nice, round fraction of the pyramids base measurement in inches...36288 ÷ 51.84 = 700.
Now regarding Herodotus's second statement that, 'the surface area of each face was equal to the square of the height':
The Great Pyramid, unlike its smaller companions, was purposely built to have a flat top. The reason for this is that it was necessary to have a "Holies of Holies" altar, where all 4 quarters of the Earth could be viewed simultaneously. From this altar or "plane table", very accurate calculations could be made on the alighting or ascending positions of stars through 360 degrees of arc. To make these determinations the astronomer/ mathematicians worked from a terrace set exactly to the 450 feet level. The altar/ plane table extended 3 feet above this level and the astronomers knelt on the terrace to view across the expanse of the table at the ascending or descending stellar positions. Taut string lines traversing the geometric patterning on the table or a range of other devices, allowed for accurate degree angle fixes onto the target stars.
Despite the fact that
the Great Pyramid was built without a capstone, it was still possible to include
a theoretical one in ongoing calculations or coding, based upon where lines
up the face from the bottom converged at a common point above the pyramid.
Considering that the base length was 756 feet and the face angle 51.84 degrees,
the point where all lines converged above the pyramid was, essentially, 480
feet of vertical height. Any marginal residue beyond 480 feet would likely
have been trimmed, as 480 was the sought after code for vertical height.
Therefore, Herodotus was correct in that this vertical height "squared" is
equal to the surface area of each face... 480 ft X 480 ft = 230400 sq. ft.
THE CODED PHI ANGLE & THE PHI BASED PYR. ACRE CODE.
If one uses simple trigonometry
to work out the side length of the full pyramid, including the theoretical,
non-existent capstone, the length to the centre apex would be (Adj. ÷ 51.84
Cos.) = 611.7894615 feet.
Alternatively, if one used a PHI method of Adj. (378 feet) X PHI (1.6180339)
= 611.6168142 feet.
It will be observed that the calculated PHI length is only about 2 inches
less than the length achieved by straight trigonometry. The ancient astronomer/
mathematicians were coding a PHI related angle for the Great Pyramid simultaneously
to the standard angle of 51.84-degrees. The whole edifice was designed to
clearly code PHI relationships. For example:
Let's consider the Great
Pyramid on the basis of PHI and the ratio relationship (in pyramid acres)
between the 4 faces, compared to the ground area that the Great Pyramid covers.
The surface area of each face of the theoretical full pyramid, complete with
a (symbolic) pointed capstone, = 611.6168142 feet of side length X 378 feet
(1/2 the base length) = 231191.11558 square feet.
Because there are 4 faces,
their combined square footage amounts to 924764.6231 square feet. This translates
to 32.10988275 pyramid acres of 28800 square feet each.
The base area measured 756 feet X 756 feet or 571536 feet, which equated to
19.845 pyramid acres of 28800 sq. ft each. A perfect PHI relationship exists
between this (symbolic capstone included) total side acreage and that of the
base: 32.10988275 ÷ 19.845 = 1.6180339 (PHI).
THE PI CODE.
A nigh-on
perfect Pi code is also built into the vertical height of the Great Pyramid,
based upon the slope angle up the diagonal faces of 51.84-degrees and a base
side length of 756'. Under such circumstances, lines coming up each of the
four faces would intersect at a vertical height of 481.04297651 feet.
Two side lengths
at the base of the pyramid would equate to 1512' (756' X 2). Therefore: 1512'
÷ 481.04297651' (vertical height) = 3.14317. Under such close proximity
circumstances a perfect Pi relationship would exist if the pyramid achieved
a height 2.88-inches greater in this symbolic geometric relationship between
vertical height and two base side lengths.
THE 11.52 CODE.
This particular number is of such immense importance that it will be found encoded, somewhere, within the larger standing stone circles or communal structures of antiquity. The number had a very significant purpose and universal application, which was:
The Heliacal or Sothic
rise of the binary star, Sirius, occurs at a measurable interval of every
365.25 days and this event almost perfectly describes the duration of the
true solar year. The Heliacal rise of Sirius, therefore, represented a gauge,
by ancient astronomers, for a close approximation coding of the count of days
in a year.
They did, however, know that the figure was slightly incorrect and so introduced
a number, which could be used to correct the Sirius year. The amount of time
required to deduct from the Sirius year, by their system, was 11.52 minutes,
rendering the solar year as 365.2420 days...the exact figure occurring on
the Mayan calendar.
It will be demonstrated, as we proceed, that this number, 11.52, is integral
to the Menkaure Pyramid, but for the moment, let's extract it from the dimensions
of the Great Pyramid.
1. The coded lengths up the side of the diagonal faces of the Great Pyramid were 576 feet...this is 1/2 of 1152.
2. Just as the sum of 51.84 was 1/500th of the 25920-year duration of the Precession of the Equinoxes, if the sum of 576 feet of diagonal side length is reduced to 1/500th of its value, the total is 1.152 feet.
3. It has been shown, mathematically, that the true square footage value for a face of the Great Pyramid was 230400 sq. ft. This is 115200 X 2.
The numbers 1.152, 11.52, 115.2, 1152 or larger expressions, will be seen to recur prolifically from Egypt to Stonehenge, then into the Pacific. This is a truly dynamic astronomical number, related to 288 and 5184. It is an important calibration increment coded into the Sarsen Circle at Stonehenge, where the total circumference (345.6 feet) is 11.52 feet per lintel (30 lintels) or 360 (degrees) X 11.52 inches per degree of arc.
THE 1728 CODE.
Again, this is one of the big codes of antiquity and is virtually guaranteed to be found encoded into every large astronomically/ navigationally based site. It is extractible amidst the 1100 standing stones of Le Menec, Brittany, France, where it provides a founding principle upon which the entire site was built. The same holds true of Silbury Hill.
The reason 1728 is so
important relates to the wonderful relationship that occurs between it and
a PI reduction, which goes: A 1728 circumference ÷ 3.1416 (PI) = 55.00381971
diameter. This close relationship between a sexagesimal circumference converting
conveniently to a whole "11 series" number, was exploited universally in antiquity.
Many linear distances were based upon an 11 series of numbers (league, mile,
furlong, chain, rod / perch, fathom & link. The 1728 system, which incorporated
a circumference number that could be broken down sexagesimally was, exploited
for navigation. The charts would calibrate distances covered leagues (without
any doubt, 16500 feet or 3.125 miles, although lost sometime after the Roman
incursion into Great Britain). Therefore: 16500 feet X 3.1416 = 51836.4 feet...and
look again very closely at the number achieved...it is extremely close to
51840 feet. Under this excellent system, 1440 feet represented 1 degree of
arc in a circle extending through a league of diameter.
This means that the navigator could calculate the straight-line distance covered in leagues and the expanding circle would go up exponentially to the linear distance covered. Careful plotting of the expanding circumference calibration would maintain knowledge of the degree angle back to the point of origin or to the destination. Any course change would necessitate the creation of a new circle, with knowledge of degree angles to points of departure or destination, maintained by trigonometric calculations between plotted circles.
Evidence on other calibrated
circles, such as the Sarsen Circle at Stonehenge, would suggest that the ancient
navigators used a specialised and marginally adjusted expression of PI for
navigation. This was set to 3.141818182 and would always achieve a perfect,
breakdown sexagesimal circumference value in any of the 11 series linear measurements,
including the link.
It is very plausible to consider that mariner / navigators would have had
a calculation rod of 1.728 feet (20.736 inches) for geodetic, mnemonic reference.
Such a rod would be in direct ratio to the 51840 feet circumference achieved
in a diameter of 1 league...51840 ÷ 1.728 = 30000 or 51840 ÷ 20.736 (the inch
value rod would nave been 20.736") = 2500.
Some rods have been found in Egypt, which are slightly in excess of 20.7 inches
and it is now time to return to a close analysis of all rods located and the
hieroglyphics displayed above each incremental segment.
The 345.6 feet outer rim of Stonehenge would equate to 1.728 X 200 or 345.6
feet ÷ 20.736 = 16.666666666.
Remember, the adjacent in 3,4,5 triangulation is always 1.666666666 less than
the hypotenuse.
It would appear likely
that the ancient "11 series" grid referencing system segmented the Earth into
360 divisions for both latitude and longitude. A grid square, near the equator,
would, by this system, be 22 leagues or 68.75 miles. With the traversal of
1 degree of arc of 22 leagues diameter, the accompanying, associated, circle
circumference was 69.12 leagues, 216 miles, 1728 furlongs, 17280 chains, 69120
rods/ perches, 207360 fathoms or 1728000 links.
To plot 1 degree of arc on the periphery of a circle of 22 leagues diameter,
one could work in a smaller increment like chains...17280 ÷ 360 degrees
= 48 chains per degree of arc. Also, 22 leagues of diameter converts to 1140480
feet of circumference and if this is divided by 51.84 the result is 22000
divisions of 51.84 feet.
Adept navigators are encouraged to test this ancient navigational numerical
system, such that we can restore it to full knowledge and understanding. Most
of the foundation mathematical elements have been identified on the Great
Pyramid, but the fullness of practical application, upon the open sea, is
yet to be experimented with anew...and this author is a landlubber.
DETERMINING THE SPEED OF THE SUN'S PASSAGE THROUGH THE SKY AND THE DURATION OF A DAY.
It has been determined that there were a series of measuring rods in use in ancient Egypt, each of which could be pressed into service as required, depending upon the specific information sought after or codes to be extracted. Several measuring rods were in standard increments for normal measurement purposes, with yet another set, hovering between 20.59 inches to just over 20.7 inches, used specifically for geodetic purposes and navigation. This second set, comprising of at least four types of rods, became known as the "Egyptian Royal Cubits". Three of these Royal Cubit rods and their exact sizes have already been discussed at length. Let's now introduce the fourth one.
For most navigation the sexagesimal and "11" series rods were used, with the third option available to also view the circumference of the Earth in terms of pure PHI increments. Each of these systems allowed for a small degree of error in order to create a mathematical progression that was fluidly reducible down to seconds of arc. There was, however, an additional rod that gave the exact equatorial size of the Earth to within 19.2 miles of the circumference figure that we use today.
It has already been demonstrated that particular numbers were highly important to the ancient system of astronomical/ navigational calculations. Two of the very important numbers discussed are 1728 and 51.84. Particular measurements found at the base of the Great Pyramid in the "paving slab" section reveal that there was a measurement that alludes to 20 X 1.728 feet or 34.56 feet (a dynamic number incorporated into the Sarsen Circle at Stonehenge). This suggests a Royal Cubit of 1.728 feet or 20.736 inches.
When the selfsame rule of finding the size of the Earth is applied to this "Cubit" (that of multiplying the 20.735 figure by 1200 and then reading the resultant figure in miles) the total is 24883.2 miles. Inasmuch as the official figure for the equatorial size of the Earth is 24902.4 miles, the ancient shortfall is only 19.2 miles in circumference and 6 miles in diameter. In consideration of the fact that our Earth is a somewhat misshapen oblate spheroid, it all gets a little academic at these tolerances and the ancient figure is arguably about as good as the modern one.
To calculate the ancient number used to describe the speed of rotation of the Earth, simply divide 24883.2 miles by 24 hours, which equals 1036.8 MPH. This figure is 518.4 X 2 MPH and goes a long way toward explaining why the base of the Great Pyramid was 5184 square reeds, its side angle 51.84-degrees and its total Egyptian acreage 51.845 for the 4 sides and base area combined.
THE DESIGN CONFIGURATION & FUNCTIONS OF THE GREAT PYRAMID'S ALTAR.
This must rate as the most important subject for any discussion related to the Great Pyramid...just what were the astronomer/ priests doing up there on that flat floor altar? Considering that the top of the pyramid is now a jumbled mess, covered in the graffiti of many generations, is it even remotely possible to reconstruct a plausible concept of the altar's function?
It is said that mathematics
is the only eternal language that can continue to convey information, long
after the meanings of phonetic or hieroglyphic symbols have receded from memory.
Via the medium of mathematics we are able to see, beyond any reasonable doubt,
what kinds of endeavours were pursued atop the Great Pyramid. This is because
the physical dimensions of the area limit the possibilities to a few specific
functions.
We may also ask the question, what was of utmost importance to this civilisation...what do comparative analysis clues tell us regarding their primary preoccupations and perceived greatest needs?
* We know that they were a highly mobile people, plying the trade routes of antiquity and using the ocean's as highways to far flung destinations.
* We know they were going to the Pacific coast of South America, based upon the tobacco and nicotine residues found in pre-Dynastic Egyptian mummies or the cocaine that had been ingested as a painkiller for the terminally ill. They got to China in consideration of the silk woven into the hair of some mummies.
* We know they got into the vicinity of Australia because of the Eucalyptus oil used in embalming or the mummified marsupials, reportedly, found in some Egyptian tombs. Carter found 11 gold inlaid boomerangs in Tutankhamun's tomb...so who had the boomerang first and was it introduced to Australia by the Egyptians or vice versa?

Figure 6: These 11 boomerangs were found in Tutankhamun's tomb by Carter. An ancient boomerang was also found in a midden at Murawai Beach, near Auckland, New Zealand in 1925 by Mr. A.W.B. Powell. Did cultural knowledge related to this enigmatic Murawai Beach artefact come to New Zealand by way of Australia or directly from the Near East?
* We can identify, from their mathematics, what their geodetic, world navigating systems were and how they got from place to place, while accurately plotting their relative position and progress enroute. Their navigators would play out knotted ropes astern, from time to time, to gauge relative speed through the water (thus the question...'how many knots are we going Boson?'). The navigators would constantly be doing mental arithmetic, taking in account sea currents, wave angle, wind shear etc., such that an accurate assessment of relative position could be maintained, day and night.
* Inasmuch as mathematical formulas, to do with the base perimeter measurement, the vertical height, the pyramid's angle, the size of the top floor or playoffs between these attributes, accentuate "ring of the Earth" measurements, it seems almost obligatory that geodetic systems would be found encoded into the top altar.
* We know these ancient people were avid astronomers and were making such difficult measurements as the Precession of the Equinoxes or the recurrence of solar and lunar eclipses. They were observing the transits of Venus and Mercury, the eclipsing of stars by the planets and calculating the time-span between any and all such occurrences or other celestial events.
* For their complex astronomical work we know that they used star and cross pattern geometry, which also incorporated PHI vectors overlaid by PHI diminishing concentric circles and squares. This universally used pattern system was so versatile it could be applied to setting out an observatory at any latitude of the Earth. The overlaying patterns finally culminated into a 64 square calculation matrix and this was the origin of our modern day chessboards. To the outer peripheral squares of the chessboard was added a chevron pattern, which provided 9 segments per side, related to calculating the positions of the zodiacal constellations. Again it seems almost obligatory that the 64-square matrix be found marked into the pyramid's altar.
* Many tens of thousands of mummies were laid to rest during the late Dynastic period of Egyptian history with a hypocephalus amulet placed beneath the head. An amazing similarity exists between the Amon-RA figure of the Hypocephalus and the geometry occurring at the corners of the 64 square calculation matrix. The long feathers extending from the plumed crown of Amon-RA, as found on statuette effigies of the Sun God, rise on a diagonal then return back downward on another diagonal. This is a duplication of what occurs with the rays of the 12-pointed star in the corner geometry of the 64-square matrix. The many comparable features, between funeral scribe or purely geometric depictions, are sufficient to suggest that the symbolic attributes of Amon-RA were derived from the universal geometry, then metamorphasised into the traditional physical characteristics of Amon-RA.
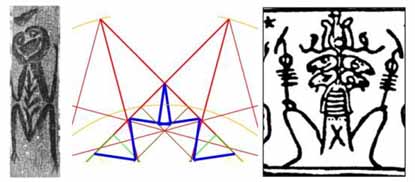
Figure 7: The centre figure occurs naturally as a result of the universal astronomical pattern geometry. To the left is a Moriori tree trunk carving from the Chatham Islands of New Zealand and to the right is a funerary scribe's Amon-RA depiction from the Egyptian Hypocephalus amulet. For a full explanation on how late Egyptian funerary symbolism was derived from earlier astronomical and navigational sciences, see articles 1-6 of this website.